|
Goldenseal | |
|---|---|
Hydrastis canadensis[1]
| |
| حالة الحفظ | |
 تبدو آمنه (NatureServe)[2] |
|
| المرتبة التصنيفية | نوع |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| المملكة: | نباتae |
| غير مصنف: | كاسيات البذور |
| غير مصنف: | ثنائيات الفلقة الحقيقية |
| الرتبة: | حوذانيات |
| الفصيلة: | حوذانية |
| الجنس: | Hydrastis كارولوس لينيوس |
| النوع: | H. canadensis |
| الاسم العلمي | |
| Hydrastis canadensis كارولوس لينيوس |
|
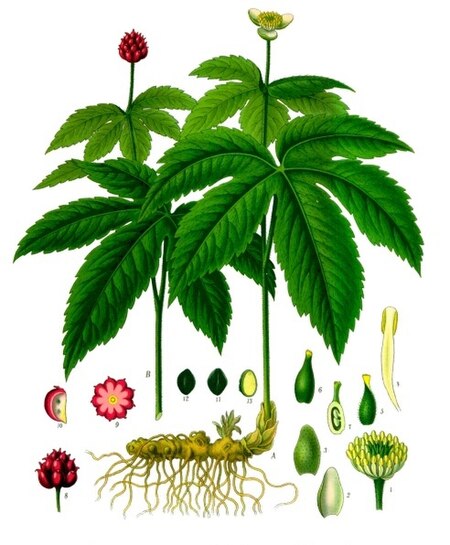
خاتم الذهب هو نبات عشبي معمر يسمى أيضاً الجذر البرتقالي موطنه جنوب شرق كندا والولايات المتّحدة الشمالية الشرقية ولكن موطنه الأصلي هو أمريكا الشمالية بشكل عام. يعتبره هنود الشيروكي وقبائل أمريكية دواءً شاملا.ويعتبر خاتم الذهب مضادا حيويا جيدا حيث تتمثل هذه القوة في مركباته الثلاثة المعروفة باسم البربرين والهيدراستين.
شكله
إنّ الجذع إرجواني وأصفر تحت الأرض حيث يوصل إلى الساق الجذري الأصفرِ. له جذر أصفر سميك وساق منتصبة يصل ارتفاعها إلى 30سم والجزء المستخدم من النبات اصلا هو الجذور.
فوائده
- يستعمل جذر خاتم الذهب كمقو جيد ومضاد للالتهابات.
- يوقف النزيف الداخلي.
- ملين ومضاد للجراثيم.
- منبه للرحم وقابض .
- يحسن من وظائف القولون والكبد والبنكرياس.
- يقتل هذا العشب البكتيريا المسببة لمرض ماحول الأسنان.
وصفات
لعلاج سوء امتصاص الغذاء يؤخذ ملء ملعقة صغيرة من مسحوق الجذر وتوضع على ملء كوب ماء مغلي ويترك لمدة 15 دقيقة ثم يصفى ويُشرب بمعدل مرتين في اليوم صباحاً ومساء.ويجب عدم استخدامه من قبل النساء الحوامل والأطفال والمرضعات.
المصادر
- Franz Eugen Köhler, Köhler's Medizinal-Pflanzen (1897)
- "Hydrastis canadensis". NatureServe Explorer. NatureServe. مؤرشف من الأصل في 18 ديسمبر 201920 مارس 2007.
- "Hydrastis canadensis". NatureServe Explorer. NatureServe. http://www.natureserve.org/explorer/servlet/NatureServe?searchName=Hydrastis+canadensis+. Retrieved on 2007-03-20.
- Foster S. and Duke J. (2000): A Field guide to Medicinal Plants and Herbs of Eastern and Central North America.New York, Houghton Mifflin
- Hoffman David (2003): Medical Herbalism. Rochester, Vermont, Healing Arts Press
- a b Hydrastis. Hydrastis canadensis. | Henriette's Herbal Homepage
- Tierra Michael (1998): The Way of Herbs. New York, Pocket Books
- Grieve M. (1971): A Modern Herbal. New York, Dover Publications, Inc
- Mills S. and Bone K. (2000): Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy. Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone
- a b http://www.med.unc.edu/phyrehab/ncmedicinalherbs/goldenseal/Goldenseal-hp.pdf
- a b c [1]Bergner, Paul Goldenseal and the Antibiotic Myth Medical Herbalism: A Journal for the Clinical Practitioner Volume 8, Number 4, Winter 1996–1997
- Rabbani, G.H., Butler, T., Knight, J., et al. Randomized controlled trial of berberine sulfate therapy for diarrhea due to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli<D> and Vibrio cholerae<D>. J Infectious Dis<D> 1987;155(5):979-984
- Weber H. A., Zart M. K., Hodges A. E., Molloy H. M., O'Brien B. M., Moody L. A., Clark A. P., Harris R. K., Overstreet J. D. and Smith C. S. (2003): Chemical comparison of goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis L.) root powder from three commercial suppliers. J Agric Food Chem. 51(25): 7352-8.
- Gentry E. J., Jampani H. B., Keshavarz-Shokri A., Morton M. D., Velde D. V., Telikepalli H., Mitscher L. A., Shawar R., Humble D. and Baker W. (1998): Antitubercular natural products: berberine from the roots of commercial Hydrastis canadensis powder. Isolation of inactive 8-oxotetrahydrothalifendine, canadine, beta-hydrastine, and two new quinic acid esters, hycandinic acid esters-1 and -2. J Nat Prod. 61(10): 1187-93
- a b Mills Simon and Bone Kerry (2000): Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy. Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone
- Lewis K. (2001): In search of natural substrates and inhibitors of MDR pumps. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 3(2): 247-54