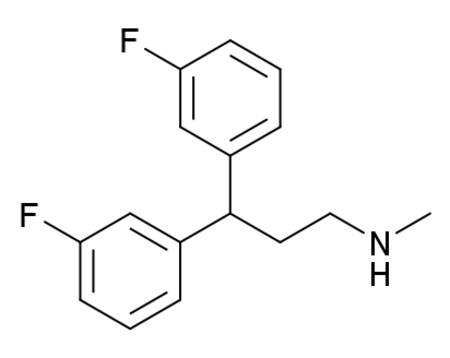
ديلوسيمين هو دواء ضاد لمستقبل NMDA ومثبط لاسترداد السيروتونين, وذو تأثيرات واقية عصبية.[1][2] أجريت عليه دراسات لاحتمال فائدته لعلاج السكتة وكذلك اجريت دراسة في عام 2004 حول احتمال مفعوله المضاد للاكتئاب.[3][4][5]
| ديلوسيمين | |
|---|---|
| الاسم النظامي | |
| 3,3-bis(3-fluorophenyl)-N-methylpropan-1-amine | |
| اعتبارات علاجية | |
| معرّفات | |
| CAS | 186495-49-8  |
| ك ع ت | None |
| بوب كيم | CID 156421 |
| كيم سبايدر | 137745  |
| المكون الفريد | 124LSR3H2X  |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106165  |
| بيانات كيميائية | |
| الصيغة الكيميائية | C16H17F2N |
| الكتلة الجزيئية | 261.3097 g/mol |
الأصل
أساس جزيئة ديلوسيمين جاء من أرجيوتوكسين 636, أما التأثير الضاد لمستقبل NMDA فهو من سم عنكبوت Argiope aurantia.[6][7][8]
المصادر
- Mueller AL, Artman LD, Balandrin MF, Brady E, Chien Y, Delmar EG, George K, Kierstead A, Marriott TB, Moe ST, Newman MK, Raszkiewicz JL, Sanguinetti EL, van Wagenen BC, Wells D (December 1999). "NPS 1506, a novel NMDA receptor antagonist and neuroprotectant. Review of preclinical and clinical studies". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 890: 450–457. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08023.x. PMID 10668449. مؤرشف من الأصل في 5 مارس 2016.
- Matthew J. Leoni; Xiao-Han Chen; Alan L. Mueller; Jessica Cheney; Tracy K. McIntosh; Douglas H. Smith (December 2000). "NPS 1506 attenuates cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal neuron death following brain trauma in the rat". Experimental Neurology. 166 (2): 442–449. doi:10.1006/exnr.2000.7513. PMID 11085909. مؤرشف من الأصل في 10 يناير 2020.
- NPS Pharmaceuticals Inc. NPSP Quarterly Report - تصفح: نسخة محفوظة 10 يناير 2020 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- Robert Pyke, Angelo Ceci. "Patent CA 2599721 A1 - Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and/or prevention of depression". مؤرشف من الأصل في 26 أبريل 201624 يونيو 2015.
- Fumito Ichinose; Eizo Marutani; Kotaro Kida. "Patent WO 2014015047 A1 - Compositions and methods to treat neurodegenerative diseases". مؤرشف من الأصل في 27 مايو 201624 يونيو 2015.
- Nentwig, Wolfgang (2013-02-15). Spider Ecophysiology. Springer Science & Business Media. . مؤرشف من الأصل في 10 مايو 2016.
- Vera Oldrati; Estelle Bianchi; Reto Stöcklin (February 2013). "Spider Venom Components as Drug Candidates". Spider Ecophysiology: 491–503. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-33989-9_37. مؤرشف من الأصل في 9 يونيو 2018.
- Victoria Monge-Fuentes; Flávia Maria Medeiros Gomes; Gabriel Avohay Alves Campos; Juliana de Castro Silva; Andréia Mayer Biolchi; Lilian Carneiro dos Anjos; Jacqueline Coimbra Gonçalves; Kamila Soares Lopes; Márcia Renata Mortari (August 2015). "Neuroactive compounds obtained from arthropod venoms as new therapeutic platforms for the treatment of neurological disorders". Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins including Tropical Diseases. 21 (31). doi:10.1186/s40409-015-0031-x. PMC . PMID 26257776.