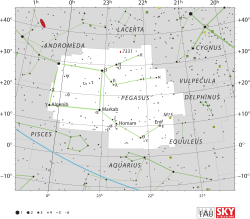
أو مو الفرس الأعظم Mu Pegasi اسمه التقليدي Sadalbari مشتق من الاسم العربي وهو نجم في كوكبة الفرس الأعظم .
| سعد بارع | |
|---|---|
كوكبة الفرس الأعظم - سعد بارع في الدائرة الحمراء(μ)
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة حقبة اعتدالان حقبة |
|
| كوكبة | الفرس الأعظم |
| مطلع مستقيم | 22س 50د 00.19315ث[1] |
| الميل | ° +24 ′36 ″05.6984[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 3.514[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | G8 III[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +0.674[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +0.932[2] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +13.54 ± 0.20[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | +144.70[1]–41.87[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 30.74 ± 0.27 د.ق |
| البعد | 106٫1 ± 0٫9 س.ض (32٫5 ± 0٫3 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | 0.432[5] |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 1.3[6] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 9.6 ± 0.4[7] نق☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 2.50[3] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 4,950[3] ك |
| معدنية (فلك) [Fe/H] | –0.03[3] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 4.0[8] كم/ثا |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| μ Peg, 48 Peg, مسح بون الفلكي+23 4615, فهرس النجوم الأساسية 862, GJ 4298, فهرس هنري درابر 216131, هيباركوس 112748, فهرس النجم الساطع 8684, فهرس مرصد سميثسونيان للفيزياء الفلكية 90816.[9] | |
ينتمي إلى الفئة الطيفية M2 و يملك قدر ظاهري 3.5 و يبعد حوالي 108 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض
مقالات ذات صلة
موسوعات ذات صلة :
مراجع
- van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- Jennens, P. A.; Helfer, H. L. (September 1975), "A new photometric metal abundance and luminosity calibration for field G and K giants.", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 172: 667–679, Bibcode:1975MNRAS.172..667J, doi:10.1093/mnras/172.3.667
- Frasca, A.; et al. (December 2009), "REM near-IR and optical photometric monitoring of pre-main sequence stars in Orion. Rotation periods and starspot parameters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 508 (3): 1313–1330, Bibcode:2009A&A...508.1313F, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913327
- Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005), "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 430 (1): 165–186, arXiv:, Bibcode:2005A&A...430..165F, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272
- Mishenina, T. V.; et al. (September 2006), "Elemental abundances in the atmosphere of clump giants", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 456 (3): 1109–1120, arXiv:, Bibcode:2006A&A...456.1109M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065141
- Smith, G. (November 1998), "Stellar atmospheric parameters for the giant stars MU Pegasi and lambda Pegasi", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 339: 531–536, Bibcode:1998A&A...339..531S
- Nordgren, Tyler E.; et al. (December 1999), "Stellar Angular Diameters of Late-Type Giants and Supergiants Measured with the Navy Prototype Optical Interferometer", The Astronomical Journal, 118 (6): 3032–3038, Bibcode:1999AJ....118.3032N, doi:10.1086/301114
- Massarotti, Alessandro; et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal, 135 (1): 209–231, Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209
- "48 Peg -- High proper-motion Star", SIMBAD, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, مؤرشف من الأصل في 26 يناير 2020,28 يناير 2012