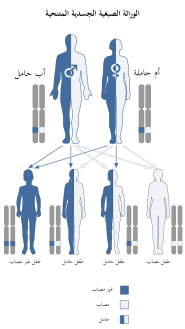
متلازمة سكوت اضطراب نزيف نادر بسبب خلل في آلية الصفائح الدموية المطلوبة لتخثر الدم.[1]
| متلازمة سكوت | |
|---|---|
تورث هذه المتلازمة بصورة متنحية
| |
| معلومات عامة | |
| من أنواع | اعتلال خثري |
عادة عند إصابة الأوعية الدموية يحدث تنشيط للصفائح الدموية كما يتم نقل فسفاتيديل سيرين (PS) في الجزء الداخلي من الصفائح الدموية إلى الجزء الخارجي من الصفائح الدموية، حيث توفر موقع اتصال لتجمعات بروتين البلازما التي تشارك في تحويل البروثرومبين إلى ثرومبين.[2]
في متلازمة سكوت، تكون آلية نقل الفسفاتيديل سيرين إلى غشاء الصفائح الدموية معطلة، مما يؤدي إلى ضعف في تكوين الثرومبين.[3][4][5] عيب مماثل في نقل الفسفاتيديل سيرين يظهر أيضا في متلازمة سكوت في خلايا الدم الحمراء وتحويل فيروس إبشتاين بار للخلايا الليمفاوية، مما يشير إلى أن الخلل في متلازمة سكوت يعكس طفرة في الخلايا الجذعية التي تؤثر على العديد من مكونات الدم.
أساس الخلل في نقل الفسفاتيديل سيرين غير معروف في الوقت الحاضر.[6] البروتينات التي يمكن أن تشارك في هذه العملية تبدو طبيعية في الصفائح الدموية في متلازمة سكوت.[7] العيوب الأخرى المحتملة في نقل الفسفاتيديل سيرين المذكورة في بعض المرضى تتطلب مزيدا من الدراسة.[8]
المراجع
- Weiss HJ. Scott syndrome: a disorder of platelet coagulant activity (PCA). Sem Hemat 1994; 31:312-319
- Zwaal FA, Comfurius P, Bevers EM. Scott syndrome, a bleeding disorder caused by defective scrambling of membrane phospholipids. Biochem Bioph Acta 2004; 1636:119-128
- Rosing J, Bevers EM, Comfurius P, Hemker HC, von Dieijen G, Weiss HJ, et al. Impaired factor X and prothrombin activation associated with decreased phospholipid exposure in platelets from a patient with a bleeding disorder. Blood 1985; 65:1557-1561.
- Toti F, Satta N, Fressinaud E, Meyer D, Freyssinet JM. Scott syndrome, characterized by impaired transmembrane migration of procoagulant phosphatidylserine and hemorrhagic complications, is an inherited disorder. Blood 1996; 87:1409-1415
- Elliott JI, Mumford AD, Albrecht C, Collins PW, Giddings JC, Higgins CF et al. Characterization of lymphocyte responses to Ca2+ in Scott syndrome. Thromb Haemost 2004; 91:412-415
- Sims PJ, Wiedmer T. Unraveling the mysteries of phospholipid scrambling. Thromb Haemost 2001; 86:266-275
- Zhou Q, Sims PJ, Wiedmer T. Expression of proteins controlling transbilayer movement of plasma membrane phospholipids in the B lymphocytes from a patient with Scott syndrome. Blood 1998; 92:1707-1712
- Weiss, HJ: Impaired platelet procoagulant mechanisms in patients with bleeding disorders. Sem. Thromb. Hemost. 35:233-241, 2009
مزيد من القراءة
- Heemskerk JWM, Bevers EM, Lindhout T. Platelet activation and blood coagulation, Thromb Haem 2002; 88:186-194
- Martinez MC, Martin S, Toti F, Fressinaud E, Dachary-Prigent J, Meyer D, et al. Significance of capacitative Ca2+ entry to the regulation of phoshatidylserine expression at the surface of stimulated cells. Biochemistry 1999; 38:10092-10098
- Munnix ICA, Harmsma M, Diddings JC, Collins PW, Feijge P, Comfurius JWM, et al. Store-mediated Ca2+ entry in the regulation of phoshatidylserine exposure in blood cells from Scott patients. Thromb Haemost 2003; 89:687-695
- Weiss HJ, Vicic WJ, Lages BA, Rogers J. Isolated deficiency of platelet procoagulant activity. Am J Med 1979; 67:206-213
- Miletich JP, Kane WH, Hofmann SL, Stanford N, Majerus PW. Deficiency of factor Xa-factor Va binding sites on the platelets of a patient with a bleeding disorder. Blood 1979; 54:1015-1022
- Bevers EM, Wiedmer T, Comfurius P, Shattil SJ, Weiss HJ, Zwaal RFA, et al. Defective Ca2+ induced microvesiculation and deficient expression of procoagulant activity in erythrocytes from a patient with a bleeding disorder: a study of the red blood cells of Scott syndrome. Blood 1992;79:380-388
- Kojima H, Newton-Nash D, Weiss HJ, Sims PJ, Zhao J, Wiedmer T. Production and characterization of transformed B-lymphocytes expressing the membrane defect of Scott Syndrome. J Clin Invest 1994; 94:2237-2244
- Stout JG, Basse F, Luhm RA, Weiss HJ, Wiedmer T, Sims PJ. Scott syndrome erythrocytes contain a membrane protein capable of mediating Ca2+-dependent transbilayer migration of membrane phospholipids. J Clin Invest 1997; 99:2232-2238
- Albrecht C, McVey JH, Elliott JI, Sardini A, Kasza I, Mumford AD, et al. A novel missense mutation in ABCA1 results in altered protein trafficking and reduced phosphatidylserine translocation in a patient with Scott syndrome. Blood 2005; 106:542-549
- Brooks MB, Catalfamo JL, Alex Brown H, Ivanova P, Lovaglio J. A hereditary bleeding disorder of dogs caused by a lack of platelet procoagulant activity. Blood 2002; 99:2434-2441