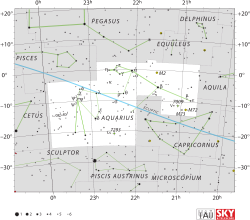
أو دلتا الدلو Delta Aquarii له اسم تقليدي Skat مشتق من الاسم العربي. وهو نجم في كوكبة الدلو .
| الساق | |
|---|---|
نجم الساق في الدائرة الحمراء
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | الدلو |
| مطلع مستقيم | 22س 54د 39.0125ث[1] |
| الميل | ° −15 ′49 ″14.953[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 3.252[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | A3 V[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +0.172[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +0.068[2] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +18.0[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | -42.60[1]-27.89[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 20.44 ± 2.26 د.ق |
| البعد | approx. 160 س.ض (approx. 49 ف.ف) |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 2.0[5] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 2.4[5] نق☉ |
| ضياء | 26[5] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 3.66[6] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 9,000[6] ك |
| معدنية (فلك) [Fe/H] | –0.15[6] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 81[7] كم/ثا |
| عمر | 0.3[8] ج.سنة |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Skat, Scheat, 76 Aquarii, BD-16 6173, فهرس النجوم الأساسية 866, HD 216627, هيباركوس 113136, HR 8709, SAO 165375.[9] | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| سيمباد | بيانات |
يعتقد أن الساق عضو في مجموعة الدب الأكبر المتحركة. يملك الساق قدر ظاهري 3.269 ويبعد عن الأرض 160 سنة ضوئية.[1]
خصائص
خيوط طيفه تطابق التصنيف النجمي من A3 V مما يشير على انه نجم من نوع-A من النسق الأساسي يولد طاقة من خلال الاندماج النووي للهيدروجين في نواته. لديه ضعف كتلة الشمس و 2.4 من نصف قطرها . و يشع 26 مرة أكثر من الشمس، غلافه الخارجي عند درجة حرارة فعالة نحو 9000 كلفن تعطيه لون ابيض مميزة، يمتلك النجم سرعة دوران عالية نسبيا تصل إلى 81 كم ثا−1
النجم لا يبعث إشارة قوية للأشعة تحت الحمراء التي قد تدل على وجود المادة حوله . يقدر عمر نجم الساق ب 500 مليون سنة ومن المحتمل انه عضوا في مجموعة الدب الأكبر المتحركة .
مقالات ذات صلة
المراجع
- van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- Celis S., L. (October 1975), "Photoelectric photometry of late-type variable stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 22: 9–17, Bibcode:1975A&AS...22....9C
- Houk, Nancy (1979), Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars, 4, Ann Arbor, Michigan: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Bibcode:1988MSS...C04....0H
- Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities. Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington. Bibcode:1953QB901.W495.....
- Malagnini, M. L.; Morossi, C. (November 1990), "Accurate absolute luminosities, effective temperatures, radii, masses and surface gravities for a selected sample of field stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 85 (3): 1015–1019, Bibcode:1990A&AS...85.1015M
- Hill, G. M. (February 1995), "Compositional differences among the A-type stars. 2: Spectrum synthesis up to V sin i = 110 km/s", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 294 (2): 536–546, Bibcode:1995A&A...294..536H
- Royer, F.; Zorec, J.; Gómez, A. E. (February 2007), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. III. Velocity distributions", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 463 (2): 671–682, arXiv:, Bibcode:2007A&A...463..671R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224
- Ehrenreich, D.; et al. (November 2010), "Deep infrared imaging of close companions to austral A- and F-type stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 523: A73, arXiv:, Bibcode:2010A&A...523A..73E, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014763
- "del Aqr -- Star", SIMBAD, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, مؤرشف من الأصل في 11 ديسمبر 2019,30 يناير 2012
- ^ Allen (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning. New York: Dover Publications. .